|
|
 发表于 2022-12-22 19:38:27
|
显示全部楼层
发表于 2022-12-22 19:38:27
|
显示全部楼层
磁盘文件
文件、页面、记录
记录
这些记录被组织成关系(表).
页码
- 磁盘的基本数据单位是页,这是从磁盘到内存的最小传输单位,反之亦然.
每个关系都存储在自己的文件中,其记录被组织到文件中的页面中.
其他
根据关系模式和访问模式,数据库将确定:
- 使用的文件类型,
- 如何在文件中组织页面,
- 如何在每页上组织记录,
- 以及每条记录的格式.
文件类型
对于每个关系,数据库根据关系访问模式的 I/O 成本选择要使用的文件类型.
1 I/O 相当于从磁盘读取 1 页或写入磁盘 1 页,并且根据其访问模式中的插入、删除和扫描操作为每个文件类型进行 I/O 计算.
堆文件
堆文件是页面或页面上记录没有特定顺序的文件类型,具有两种实现形式(链表实现和数据页实现).
链表实现
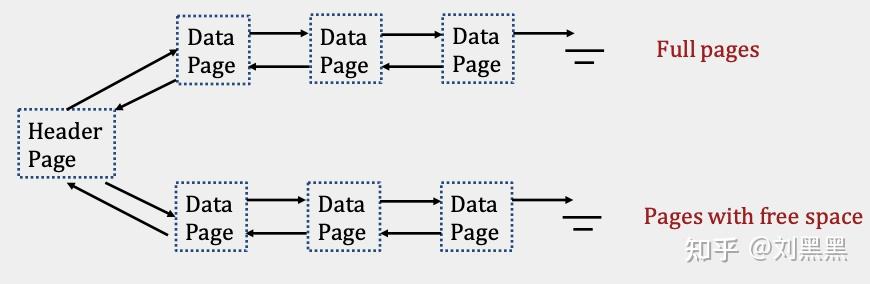
必要的变量
- 一个头指针页(充当文件的开头,并将数据页分为完整页和空闲页)
- 数据页
- 记录内容
- 指向自由空间的指针
- 指向下一页和上一页的指针
一些具体操作
- 当需要空间时,将分配空页面并将其附加到列表的空闲页面部分.
- 当可用数据页变满时,它们将从可用空间部分移动到链表的完整页部分的前面(头插法).另一种方法是在头指针页中保留指向此列表末尾的指针.
页面目录实现
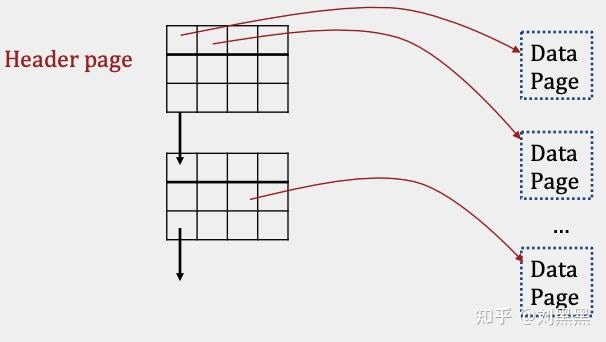
必要的变量
- 数据页
- 头节点页
- 指向下一头指针页的指针
- 指向数据页的指针以及该数据页的空余空间量
两种实现的比较
链表实现
页面目录实现
与链表相比,页面目录的主要优点是插入记录通常更快.
排序的文件
排序文件是一种文件类型,其中页面是按顺序排列的,每个页面中的记录是按键排序的. 这些文件是使用页面目录实现的,并根据记录的排序方式对数据页面强制排序.
- 搜索时间复杂性:O(logn)
- 插入时间复杂性:O(n+logn)
关于头指针计数的说明
问题:是否考虑访问文件中标题页的成本?
- 提供特定的文件实现:必须包括与读/写文件头页相关的 I/O 成本
- 不提供底层实现:您应该忽略与读/写文件头页相关的 I/O 成本
记录类型
固定长度记录(FLR)
仅包含固定长度字段(整数、布尔值、日期等)
可变长度记录(VLR).
VLR 包含固定长度和可变长度字段(例如 varchar)
VLR 将所有固定长度字段存储在可变长度字段之前,并使用包含指向可变长度字段末尾的指针的记录头.
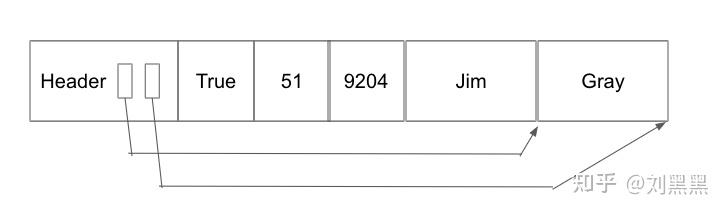
无论格式如何,每条记录都可以通过其记录 id-[page #,record # on page]进行唯一标识.
页面格式
具有固定长度记录的页面
使用头指针来存储页面上当前的记录数.
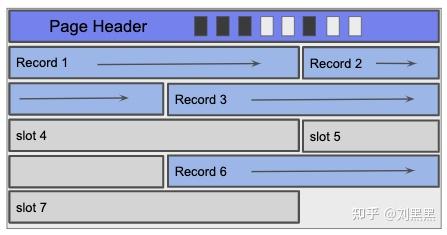
密集页面
- 插入简单,我们可以使用现有记录的数量和每条记录的长度计算页面中的下一个可用位置.
- 删除稍微复杂,需要在删除的记录之后移动所有记录.
分散页面
头指针通常会存储一个附加位图,该位图将页面拆分为多个插槽,记录插槽的状态(空闲 or 被占用).
- 插入,包括查找第一个空闲位,在相应的槽中设置新记录,然后为该槽设置位值(表明已经被占用).
- 删除,我们在位图改变被删除记录的状态,以便将来的插入可以覆盖该槽.
具有可变长度记录的页面
必要的变量
- 页脚从页面底部而不是顶部开始,这样插槽目录在有记录需要按被插入时就有空间了
- 插槽目录
- 插槽计数器跟踪插槽总数,包括已填充插槽和空插槽.
- 可用空间指针指向页面中的下一个可用位置.
- 条目都由一对[记录指针,记录长度]组成.
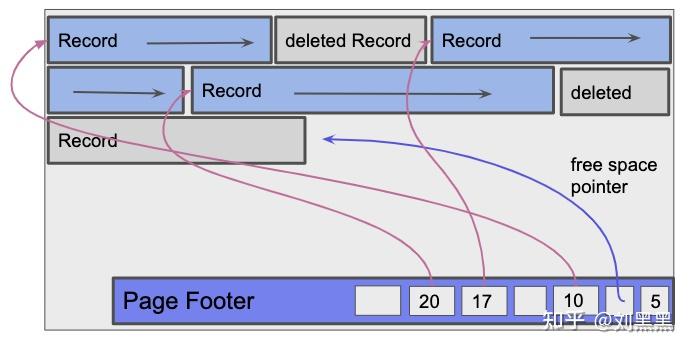
密集页面
- 插入
- 记录被插入到页面的空闲空间指针处
- 在任何可用的空条目中设置新的[pointer,length]对.如果没有空条目,则会在该记录的插槽目录中添加一个新条目.插槽计数用于确定应在哪个偏移处添加新插槽条目,然后插槽计数递增.定期将记录重新组织为密集状态,删除的记录将被删除,以便为将来的插入留出空间.
- 删除,在插槽目录中查找记录的条目,并将记录指针和记录长度设置为 null.
分散页面
- 插入,记录将插入到可用空间指针处,如果所有插槽都已满,则每次都会添加一个新条目.
- 删除,删除插槽目录中的记录条目.此外,删除记录后的记录必须向页面顶部移动一个位置,相应的槽目录条目必须向页面底部移动一个位置.
练习题
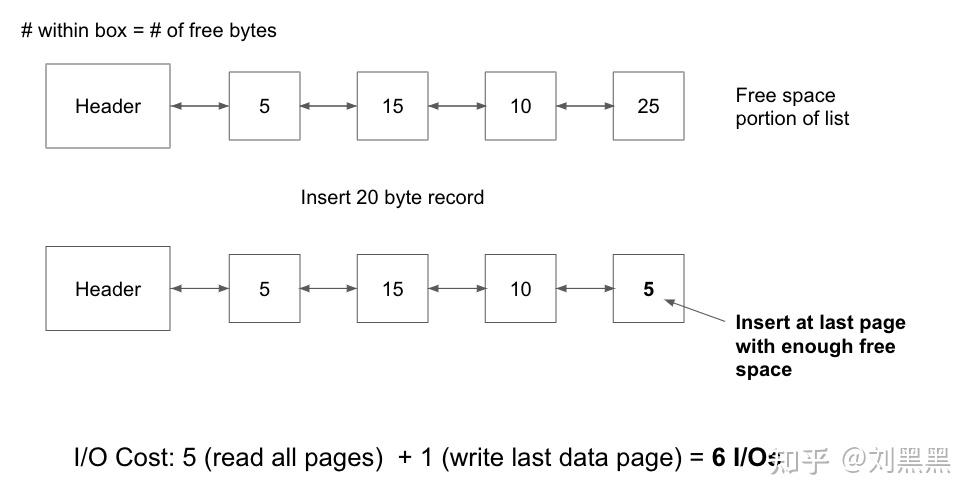
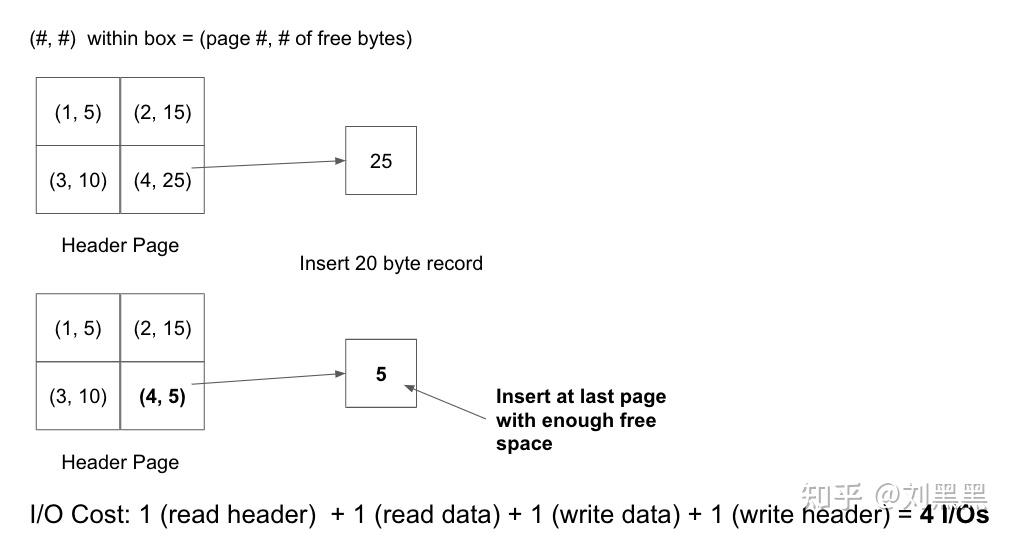
- 给定一个实现为页面目录的堆 le,插入记录的 I/O 成本在最坏的情况下是多少?目录包含 4 个标题页,每个标题包含 3 个数据页,假设至少有一个数据页有足够的空间用于记录.
在最坏的情况下,只有最后一个标题页上才有足够的可用空间. 4(读取页眉页面)+1(读取数据)+1(写入数据)+1(写入最后一个页眉)=7 因此,成本为 7 个 I/O.
- 以下模式中记录的最小大小(以字节为单位)是多少?假设记录头是 5 个字节.(布尔值=1 字节,日期=8 字节)
name VARCHAR
student BOOLEAN
birthday DATE
state VARCHAR VLR 的最小大小为 14 个字节,当名称和状态都为空时发生. 5(记录头)+1(布尔值)+8(日期)=14
- 将 4 个 VLR 插入空白页面.插槽目录的大小是多少?(整数=4 字节)假定插槽目录中最初没有插槽.
插槽目录包含插槽计数、可用空间指针和记录项指针,记录大小对.由于指针只是页面中的字节偏移量目录是 40 字节. 4(插槽计数)+4(可用空间)+(4(记录指针)+4= 40
- 假设您有一个 heap 文件,该文件是在带有标题页的链表结构中实现的连接到完整页面的链接列表,并连接到具有可用空间的页面链表.共有 10 满页和 5 非满页.在最坏的情况下,您必须阅读有多少页以查看是否有足够空间的页面来存储具有给定大小一条记录.
6-你必须阅读头指针页,然后你可能必须顺序阅读所有 5 页非满页,查看其中是否有足够的空间用于此记录,总共 6 页.
DisksFiles
Files,Pages,Records
Records
- The basic unit of data for relational databases is a record (row). These records are organized into relations (tables).
Pages
- The basic unit of data for disk is a page, the smallest unit of transfer from disk to memory and vice versa. Each relation is stored in its own file and its records are organized into pages in the file.
Other
Based on the relation's schema and access pattern, the database will determine:
- type of file used,
- how pages are organized in the file,
- how records are organized on each page,
- and how each record is formatted.
File Types
For each relation, the database chooses which file type to use based on the I/O cost of the relation's access pattern.
1 I/O is equivalent to 1 page read from disk or 1 page write to disk, and I/O calculations are made for each file type based on the insert, delete, and scan operations in its access pattern.
Heap Files
A heap file is a file type with no particular ordering of pages or of the records on pages.Heap files has two types of implementations(Linked List Implementation and Page Directory Implementation)
Linked List Implementation

Necessary variables
- one header page
- data page
- records
- a free space tracker
- pointers to the next and previous page acts as the start of the file and separates the data pages into full pages and free pages
details
- When space is needed, empty pages are allocated and appended to the free pages portion of the list.
- When free data pages become full, they are moved from the free space portion to the front of the full pages portion of the linked list. We move it to the front, so we don't have to traverse the entire full pages portion to append it. An alternative is to keep a pointer to the end of this list in the header page.
Page Directory Implementation

Necessary variables(a linked list for header pages)
- data page
- header page
- a pointer to the next header page
- a pointer to a data page and the amount of free space left within that data page
Comparison between the two Implementations
The main advantage of Page Directories over Linked Lists is that inserting records is often faster.
Linked List implementation

Page Directory Implementations

Sorted Files
A sorted file is a file type where pages are ordered and records within each page are sorted by key(s). These files are implemented using Page Directories and enforce an ordering upon data pages based on how records are sorted.
- Search time complexity:O(logn)
- Insert time complexity:O(n+logn)
A Note on Counting Header Pages
Whether or not to consider the cost of accessing the header pages in the file.
- provide a specific file implementation:you must include the I/O cost associated with reading/writing the file's header pages
- without providing the underlying implementation: you should ignore the I/O cost associated with reading/writing the file's header pages
Record Types
Fixed Length Records (FLR)
only contain fixed length fields (integer, boolean, date, etc.)
Variable Length Records (VLR).
VLRs contain both fixed length and variable length fields (eg. varchar) VLRs store all fixed length fields before variable length fields and use a record header that contains pointers to the end of the variable length fields.

Regardless of the format, every record can be uniquely identified by its record id - [page #, record # on page].
Page Format
Pages with Fixed Length Records
use page headers to store the number of records currently on the page.

packed page
- Insertion easy as we can calculate the next available position within the page using the # of existing records and the length of each record.
- Deletion is slightly trickier as it requires moving all records after the deleted record.
unpacked page
The page header typically stores an additional bitmap that breaks the page into slots and tracks which slots are open or taken.
- Insertion involves finding the first open bit, setting the new record in the corresponding slot, and then setting the bit for that slot.
- Deletion, we clear the deleted record's corresponding bit so that future inserts can overwrite that slot.
Pages with Variable Length Records
- The page footer (starts from the bottom of the page rather than the top so that the slot directory has room to grow when records are inserted)
- The slot directory
- The slot count tracks the total number of slots including both filled and empty slots.
- The free space pointer points to the next free position within the page.
- Each entry in the slot directory consists of a [record pointer, record length] pair.

packed page
- Deletion involves finding the record's entry within the slot directory and setting both the record pointer and record length to null
- Insertions
- the record is inserted into the page at the free space pointer and a new [pointer, length] pair is set in any available null entry.
- In the case where there are no null entries, a new entry is added to the slot directory for that record. The slot count is used to determine which offset the new slot entry should be added at, and then the slot count is incremented. Periodically, records will be reorganized into a packed state where deleted records are removed to make space for future insertions.
unpacked page
- Deletion involves removing the record's entry within the slot directory. Additionally, records after the deleted record must be moved towards the top of the page by one position and the corresponding slot directory entries shifted towards the bottom of the page by one position.
- Insertion, the record is inserted at the free space pointer and a new entry is added every time if all slots are full.
Practice Questions
- Given a heap file implemented as a Page Directory, what is the I/O cost to insert a record in the worst case? The directory contains 4 header pages and 3 data pages for each header page. Assume that at least one data page has enough space to fit the record.
In the worst case, the only data page with enough free space is on the very last header page. Therefore, the cost is 7 I/Os. 4 (read header pages) + 1 (read data) + 1 (write data) + 1 (write last header) = 7
- What is the smallest size, in bytes, of a record from the following schema? Assume that the record header is 5 bytes. (boolean = 1 byte, date = 8 bytes)
name VARCHAR
student BOOLEAN
birthday DATE
state VARCHAR
The smallest size of the VLR is 14 bytes and occurs when both name and state are null 5 (record header) + 1 (boolean) + 8 (date) = 14
- 4 VLRs are inserted into an empty page. What is the size of the slot directory? (int = 4 bytes) Assume there are initially no slots in the slot directory.
The slot directory contains a slot count, free space pointer, and entries, which are record pointer, record size pairs. Since pointers are just byte offsets within the page, the size of the directory is 40 bytes. 4 (slot count) + 4 (free space) + (4 (record pointer) + 4 (record size)) * 4 (# records) = 40
- Assume you have a heap file implemented in a linked list structure with the header page connected to a linked list of full pages, and connected to a linked list of pages with free space. There are 10 full pages and 5 pages with free space. In the worst case, how many pages would you have to read to see if there is a page with enough space to store some record with a given size?
6 - You have to read the header page and then you may have to sequentially read all 5 pages with free space to see if any of them have enough space for this record, for a total of 6 pages.
|
|